Hyperbolic Circles
A Euclidean circle represents a hyperboic circle if it is entirely inside the unit circle.
Here are some basic properties that stress the differences between Hyperbolic Circles and Euclidean Circles.
Euclidean Circles
- any 3 non-collinear points lie on a unique circle.
- a line and circle meet in at most 2 points.
- 2 distinct circles meet in at most 2 points.
Hyperbolic Circles
- a hyperbolic line and a hyperbolic circle meet in at most 2 points.
- 2 distinct hyperbolic circles meet in at most 2 points.
- if a hyperbolic line contains an interior point P of a hyperbolic circle, then the hyperbolic line and the hyperbolic circle meet in 2 distinct points, with P between these points
- if the hyperbolic line H meets the hyperbolic circle K in a single point P, then H is a hyperbolic tangent to K at P.
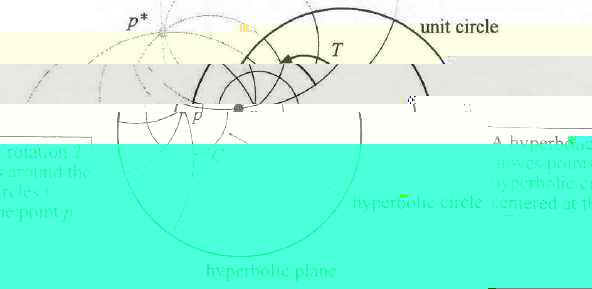
Hyperbolic Circles and Elliptic Transformations
Essential a hyperbolic circle is a curve, C, in the hyperbolic plane that is repeatedly subjected to a an elliptic transformation. Elliptic transformations have one fixed point p inside the unit disk, and another symmetrically located outside. The transformation is called a hyperbolic rotation and rotates points in the hyperbolic plane around the fixed point p. The fixed point P is the center of the curve C.
Click here to go back to the home page


